I seem to be on a roll this week, with finding incredibly interesting topics to write about over on Quora. In this case, the question was as simple as it was interesting: "Is it possible to focus an unfocused image with a computer program?".
Answer...
There are many technical challenges with focusing an image after the fact, and it depends heavily on how out-of-focus the original image is. It is possible to do some sharpening that gives the illusion of a photo being in better focus, but actually re-focusing the photo? Not so much.
Here's why...
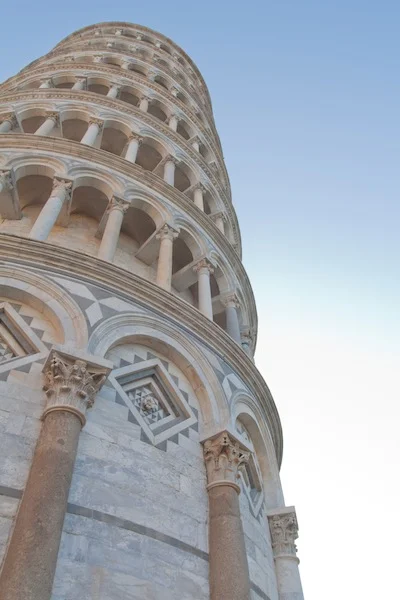
Take an image like this for example (see the photo on my Flickr stream for a larger version):
The bird in the foreground is in focus (well, more or less), but the plants in the background are not. Now, blurring this photo would be relatively trivial, because you are discarding information.
If your goal was to 're-focus' the photograph so the trees in the background were in focus, however, you're looking at a completely different problem, at least if your photo is taken with a conventional camera (Light-field cameras like the Lytro work differently)... The problem is that you're trying to re-generate information that simply isn't there.
Another example
Let's take another example. This photo, for example (see Flickr for a larger version):
In this photo, you have an extreme macro shot of a fly. You can see the individual facet eyes of the fly, and count the hairs on its back. However, it has very shallow depth of field, and if you look at the legs in the background of the photo, they are just blurry stalks. Now, the technology you are looking for, would somehow magically be able to find out the size, direction, and shape of each of the hairs on the fly's legs that are out of focus in the background.
It stands to reason that this information simply doesn't exist. I took the photo, and I have no idea what colour the hairs were, how many there were, and how evenly they were spaced. This photo is a pretty good document of the fly, of course, but it is physically impossible to recreate information that isn't there - unless you have a data source to base this information on.
On the other hand, Adobe is doing some really interesting stuff with their 'deblur' technology. This isn't the same as focus blur, however; the idea of Adobe's deblurring is to take a photo that was sharp to begin with, but suffers from motion blur. This means that, in theory, a lot of additional information exists in the image, it is just spread over an even surface. As such, it is possible to 'unblur' the image by throwing clever algorithms and a lot of computing power at the problem. Sadly, this is only possible in very limited cases. It's not possible to re-focus an image, but it is possible to evaluate the photo to remove certain image artefacts, much like noise reduction filters etc.
For further reading, check out the vaguely related concepts of Focus stacking (which uses focusing at several focus depths, and calculates an image with deeper depth of field), HDR (which does a similar thing, but for images with various exposures) and, of course, the Lytro camera, which is able to focus after the fact, but struggles with its own problems (including much lower final resolution than we are used to from our digital images).
TL;DR: No, you can't focus an image after the fact.