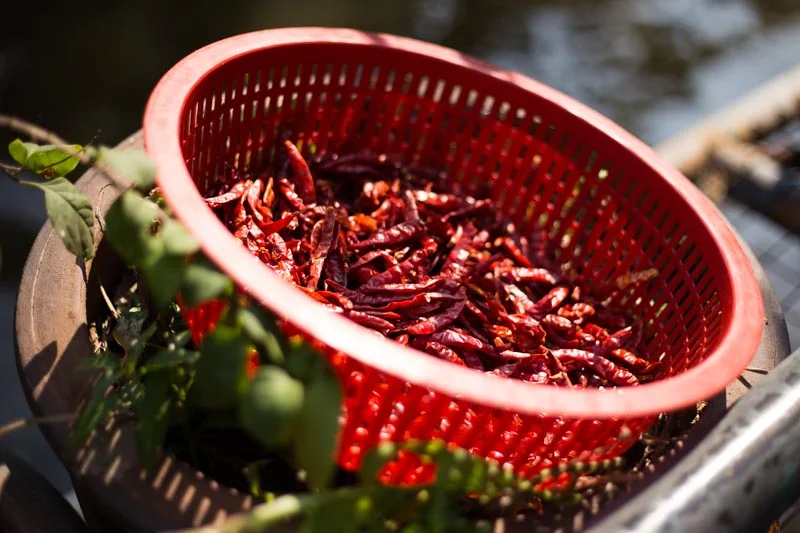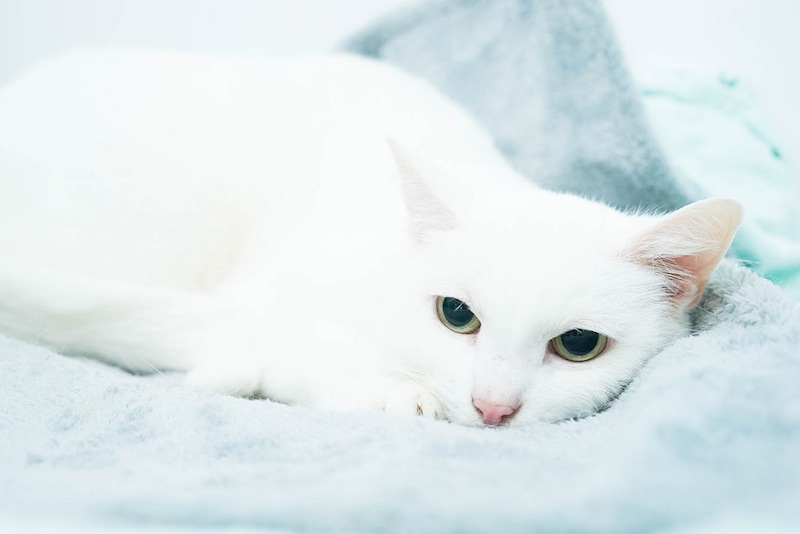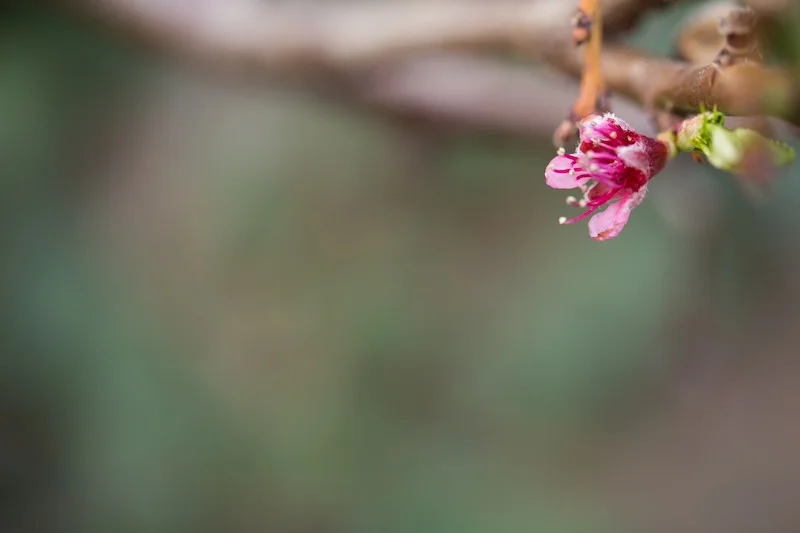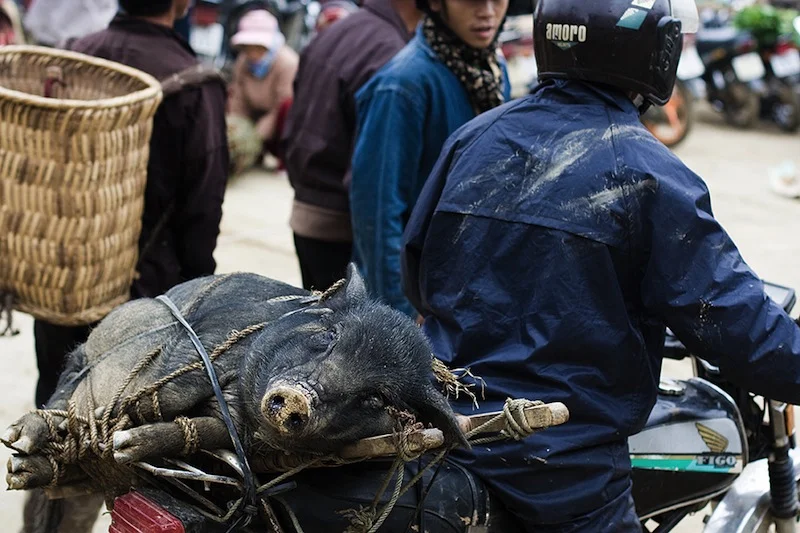
This photo was taken at broad daylight. Because I used flash and a fast shutter speed, it comes out looking like this...
I am a photo geek. I admit it. I love photography technology - especially the crazy high-tech stuff the camera manufacturers come up with. One of the most incredible pieces of electronic engineering you can buy in the photography world today is a humble flash. I'll tell you why...
In most circumstances, your flash can sync with your camera up to a certain shutter speed. back in the dawn of photography, this 'sync speed' used to be 1/60 second on most cameras. When you buy a SLR camera and a flashgun today these days, standard flash sync is 1/200th or 1/250th of a second for almost all makes and models of camera equipment.
But then, the camera boffins came up with something deeply awesome: High-speed flash sync. To understand why you need it, and to explain how and why it works we need to take a look at how flashes work normally.
How a flash works
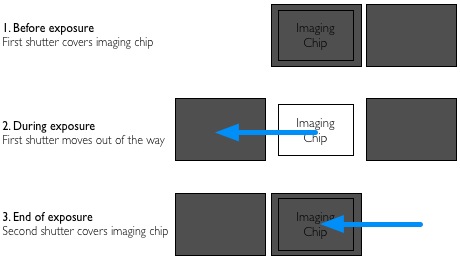
Inside your camera, there are two pieces of black fabric (known as 'curtains' - this is also where the expression 'second curtain flash' comes from) that move across the sensor at very high speed. Think of this whole set-up as a window that has two curtains that go all the way across the window. When you press the button, one curtain is pulled from left to right, and at the end of the exposure, the second curtain is pulled across to cover the window again. Once the exposure is complete, both curtains are returned to their original position on the left, ready for the next exposure.
Only a few years ago, when we were shooting on film cameras that had a manual advance lever, these curtains were on springs. When you were pulling the thumb lever to forward to the next frame on your roll of film, you would also pulling the two curtains back in preparation for the next exposure.
When your flash is in normal flash mode, the following happens: You press the shutter. The first curtain of the shutter opens fully, and the camera sends a signal to the flashes, and the flashes fire. At the end of the exposure (whether the exposure is short or long), the second curtain is pulled across to finish the exposure. If you had your camera set to 'second curtain' sync, the flash would trigger just before the closing curtain gets pulled back to cover the sensor.
Flash at higher speeds
When you start talking about very fast exposures - like the 1/8000 second exposure offered by cutting-edge SLR cameras - but basically at any speed faster than the camera's flash sync speed, something interesting happens.
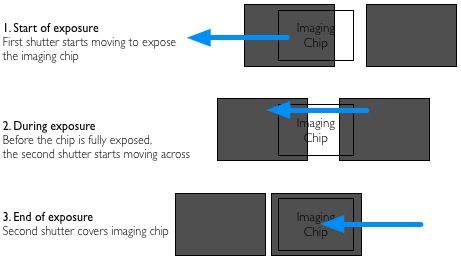
The shutter curtains themselves move incredibly fast, but when you're talking about extremely fast shutter speeds, the speed of the shutters starts to become a factor: As the shutter has to be open for such a brief period of time, the closing shutter actually starts moving before the opening shutter has finished moving. The effect is that the whole imaging chip does get the same amount of light, but the imaging sensor is never exposed all at the same time.
If you're shooting in natural light, this isn't a problem at all, but if you want to add a flash to the mix, it becomes tricky: If the shutter is never fully open, when do you fire the flashes?
The ingenious solution
Flash manufacturers realised that people still wanted to use flash even at high shutter speeds, came up with an ingenious solution: High speed sync mode, which changes the way your flash works, enabling you to take photos at much higher shutter speeds.
When the flash is set to high-speed mode, instead of a single flash once the shutter opens, the flash actually sends lots of tiny flash pulses for the duration of the exposure. This ensures that the subject is evenly lit as the shutter curtains move across the sensor: Perfect exposures even though the sensor is never open all at once!
So, is there a downside? Well, in High Speed sync mode, your flashes do take significantly more power, so you drain the batteries much faster. On the other hand, if you need it, use it: The effects can be incredible, and it gives you a lot more flexibility in your flash photography!
Now in video form!
I did a video for Gizmodo UK about high speed flash sync; in all its poorly-animated glory here:
So what can you use it for?
You can use high speed flash sync for lots of things - but start by having a look at Darkening a Room by Adding Light - that should bring you a few ideas!
Do you enjoy a smattering of random photography links? Well, squire, I welcome thee to join me on Twitter - Follow @Photocritic
© Kamps Consulting Ltd. This article is licenced for use on Pixiq only. Please do not reproduce wholly or in part without a license. More info.





