Z is for zoom. We couldn't finish off our alphabetical meander through photography's fundamentals anywhere else, could we? I've had a few people ask me, over the years, what's the difference between zoom and telephoto, and indeed is there one. Yes, yes there is a difference.
The simple explanation
Simply put, a zoom lens is one that benefits from variable focal lengths. For example, the 18-55mm kit lens that comes with an entry level dSLR is a zoom lens. At its widest point it has an 18mm focal length; at its narrowest, it has a 55mm focal length, and you can shift it to any focal length between the two. This means it spans from wide-angle to 'normal' focal lengths, giving it a fair degree of flexibility and making it useful as a first lens.
Telephoto lenses can be zoom lenses, too, for example a 70-200mm lens. Or you can have wide-angle zoom lens, for example a 17-35mm lens. Then there are zoom lenses with focal length ranges that stretch from wide-angle to telephoto, for example 24-105mm.
Whether the focal length range is wide-angle, telephoto, or spans the two is irrelevant; it's the fact that the lens covers a range of focal lengths that makes it a zoom. If you want to put it another way: a zoom lens is the opposite of a prime lens, which has a fixed focal length.
Advantages and disadvantages
The obvious advantage of a zoom lens is that it offers you flexibility. Being able to zip from 70mm right in to 200mm with the twist of the wrist is very handy, so is having wide-angle and telephoto capability in one place. And of course they let you mess around with zoom-bursting, which is always good fun.

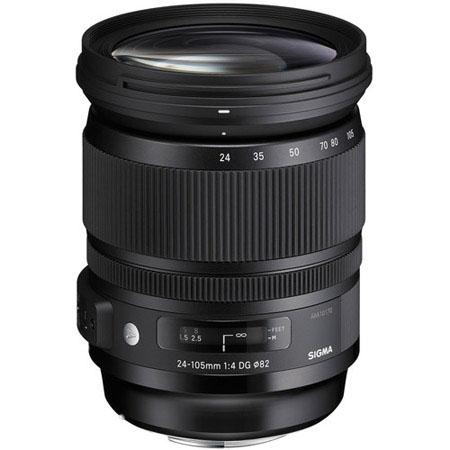
However, that flexibility comes at a cost. The moving parts required to give zoom lenses their zoom can compromise their sharpness, give them more noticable aberrations, and limit their apertures. Whereas you'll readily find prime lenses with fast apertures, zoom lenses tend to be a bit slower and they often have variable maximum apertures.
The 18-55mm kit lens that we spoke earlier won't have a fixed maximum aperture across its focal range. Instead, it will have a maximum aperture of ƒ/3.5 at 18mm and at 55mm its maximum aperture will be ƒ/5.6. That's a bit of a difference to a 50mm prime lens that has a maximum aperture of ƒ1.4, isn't it? (There are zoom lenses with constant maximum apertures, a 70-200mm ƒ/2.8, for example, but they're much more costly than variable aperture zooms.)
Finally, the more moving parts that you have, the higher the chances of something breaking. That's not limited to photographic lenses, but just about anything that you can build. In this case, however, zoom lenses are more susceptible to damage or failure than prime lenses are.
And what about digital zoom?
So far, we've talked about optical zoom, or a change in focal length that is achieved by moving parts and adjustments to lens elements within the lens body. Some cameras, however, don't have optical zoom capability and instead rely on digital zoom to bring you closer to your subject. Digital zoom is standard in smartphone cameras, but you'll often find it in compact cameras as an augmentation to their optical zoom capabilities.

Digital zoom isn't really anything other than cropping: the centre of the frame is enlarged and the edges are trimmed away. As a consequence, images that are digitally zoomed are of lower quality than full resolution photos. If at all possible, avoid using digital zoom; it won't do your photos many favours.
TL;DR
- A zoom lens is a lens with a variable focal length
- Zoom lenses can be wide-angle, telephoto, or span the range
- The advantage of a zoom lens is its flexibility, but disadvantages can include lower image quality and slower apertures
- Digital zoom isn't really zoom at all, but a form of cropping. It's best avoided.
White balance << Photography Fundamentals >> Aperture
If you want to read a much more detailed explanation of lenses, do have a look at Haje's extensive Everything about camera lenses article.








